Short-read Next-Generation Sequencing is typically performed with one round of sequencing on a single library or pool of libraries. The Max Read Kit achieves higher output by performing multiple rounds of sequencing on a single library. This is enabled by creating multiple library fractions from one input library using primers with distinct sequencing primer binding sequences (M1, M2, M3) but all containing the same clustering tags (S1 and S2; Figure 1).
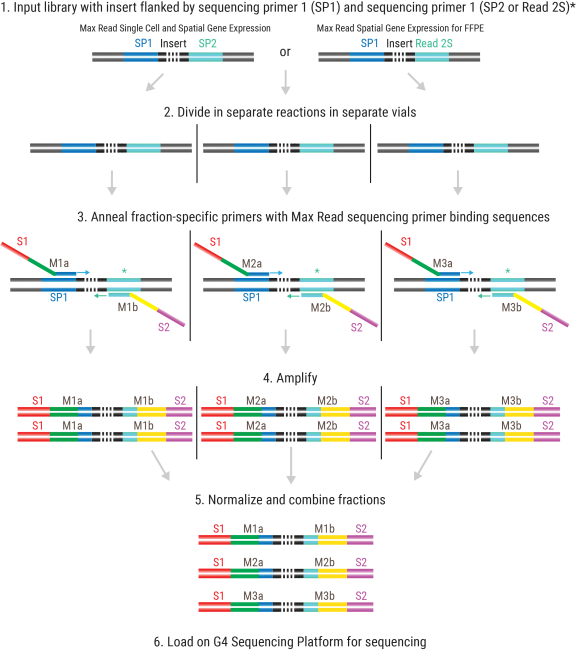
Figure 1 Overview of library preparation for Max Read sequencing. Three parallel adaptation reactions generate three different library fractions that are normalized and combined. The resulting fractions each have a different sequencing primer binding site (M1a-M3a for forward and M1b-M3b for reverse direction).
* Max Read Single Cell and Spatial Gene Expression uses SP2, and Max Read Spatial Gene Expression for FFPE uses Read 2S as reverse primer anchoring site.
After introducing the distinct sequencing primer binding sequences in the library fractions, normalize, combine fractions, and load the library onto the G4 Sequencing Platform, one Max Read library per lane since the samples are not indexed. In contrast to standard seeding in patterned flow cells which attempts to minimize poly-clonal cluster formation, the Max Read method intentionally seeds more than 1 template per nanowell, so clustering concentration is high. Perform sequencing in sequential paired read rounds with only one set of the sequencing primers per round (M1a and M1b for reads 1 and 2 in round 1, M2a and M2b for reads 1 and 2 in round 2, and M3a and M3b for reads 1 and 2 in round 3). Although nanowells can contain multiple clusters, the sequencing signal in most nanowells in a round is derived from a single clone, the one with the sequencing primer binding sites for the sequencing primers used in that round.
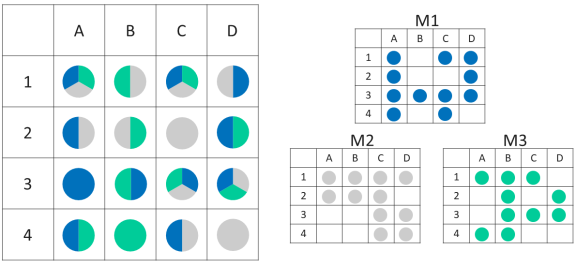
For instance, clusters in the same nanowell can be separated using the appropriate M-type sequencing primer in 3 sequential paired read sequencing rounds, as long as the clusters derive from 3 different templates, each with its own unique M-sequence tag (Figure 2).
After sequencing, the individual reads are combined into one FASTQ file set for paired read sequencing. These files are ready for standard follow-up analysis without any further changes.